Osteoarthritis Treatments: A Guide to Managing Joint Pain

Introduction
Osteoarthritis is a prevalent degenerative joint disease that affects millions of people worldwide. his condition primarily targets the cartilage that cushions the ends of bones, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced joint mobility. According to recent statistics from the World Health Organization (WHO), over 300 million individuals suffer from osteoarthritis globally. In the United States alone, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that more than 32.5 million adults have osteoarthritis, making it one of the most common chronic conditions in the country.
This condition does not discriminate based on gender, affecting both men and women. However, the CDC reports that women are more likely to develop osteoarthritis than men, particularly in the age group of 55 years and older. Among adults aged 65 years and older in the US, 53% of women and 42% of men are affected by osteoarthritis. This gender disparity could be attributed to hormonal and genetic factors that influence joint health.
Osteoarthritis is often associated with the aging process, and its prevalence tends to increase with age. According to the Arthritis Foundation, approximately 80% of people over the age of 65 have radiographic evidence of osteoarthritis, with varying degrees of symptom severity. However, it's important to note that osteoarthritis can also affect younger individuals, especially those who have experienced joint injuries or have a family history of the condition. While there is no cure for osteoarthritis, there are various osteoarthritis treatment options available to manage its symptoms effectively and improve the quality of life for individuals living with this condition.
Symptoms of Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis presents with a range of symptoms that can vary from mild to severe, depending on the individual and the affected joints. The most common symptoms include:
- Joint Pain: Pain in the affected joint is a hallmark of osteoarthritis. The pain may worsen with movement or activity and may be relieved with rest.
- Stiffness: Stiffness in the joints, especially after periods of inactivity, is a common complaint among individuals with osteoarthritis.
- Limited Range of Motion: Osteoarthritis can lead to a reduced range of motion in the affected joint, making it difficult to perform certain activities.
- Swelling and Tenderness: Inflamed joints may become swollen and tender to the touch, especially during flare-ups.
- Joint Crepitus: Osteoarthritic joints may produce a crackling or grating sound during movement, known as crepitus.
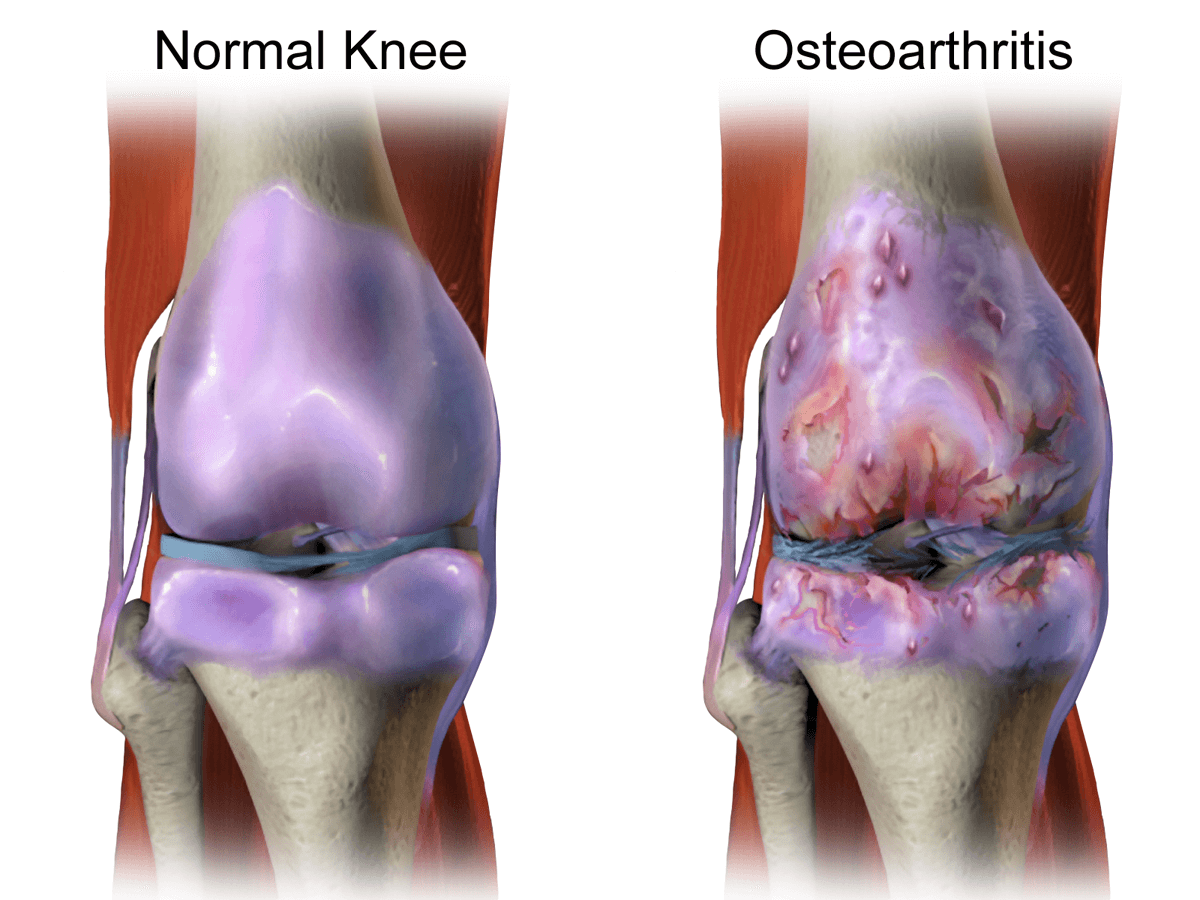
Causes of Osteoarthritis
The exact cause of osteoarthritis is not fully understood, but several factors contribute to its development:
- Age: The risk of osteoarthritis increases with age. As we get older, the cartilage in our joints naturally undergoes wear and tear, leading to osteoarthritis.
- Joint Injury or Overuse: Previous joint injuries, repetitive stress on joints, or overuse of certain joints can increase the likelihood of osteoarthritis.
- Genetics: Family history plays a role in the development of osteoarthritis. If you have a family member with the condition, you may be at a higher risk.
- Obesity: Excess body weight places additional stress on the joints, particularly in the knees and hips, contributing to osteoarthritis.
- Gender: Women are more likely than men to develop osteoarthritis, especially in the hands and knees.
- Joint Deformities: Certain congenital joint deformities or developmental conditions can predispose individuals to osteoarthritis.
Consequences of Osteoarthritis
If left untreated or poorly managed, osteoarthritis can have significant consequences on an individual's life:
- Reduced Mobility: Severe osteoarthritis can lead to joint damage and deformities, limiting an individual's ability to move freely.
- Chronic Pain: Ongoing joint pain can impact a person's quality of life, leading to decreased physical activity and potential emotional distress.
- Loss of Independence: As the condition progresses, some individuals may require assistance with daily tasks, leading to a loss of independence.
- Poor Sleep Quality: Pain and discomfort from osteoarthritis can disrupt sleep patterns, resulting in fatigue and reduced overall well-being.
- Depression and Anxiety: Dealing with chronic pain and limitations can lead to emotional challenges such as depression and anxiety.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing osteoarthritis and can significantly improve an individual's quality of life. These changes focus on promoting joint health, reducing pain, and maintaining overall well-being. Here are some key lifestyle modifications that can help individuals with osteoarthritis:
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is paramount for individuals with osteoarthritis, especially those with weight-bearing joint involvement, such as the knees and hips. Excess body weight places additional stress on the joints, accelerating the wear and tear of cartilage and exacerbating pain and inflammation. A balanced diet, rich in nutrients and low in processed foods, combined with regular exercise, can help achieve and maintain a healthy weight, easing the burden on the affected joints.
Regular Exercise and Physical Activity
Engaging in regular exercise is essential for managing osteoarthritis symptoms. Low-impact exercises, such as swimming, cycling, and walking, can improve joint flexibility, strengthen supporting muscles, and enhance overall joint function. Exercise also helps maintain a healthy weight, reduces stiffness, and increases the range of motion in affected joints. It's essential to work with a healthcare professional or physical therapist to design a tailored exercise program that suits individual needs and capabilities.
Joint Protection Techniques
Practicing joint protection techniques can minimize stress on the affected joints and alleviate pain. This involves being mindful of body mechanics during daily activities, such as lifting objects correctly and using proper posture while sitting or standing. For example, individuals with knee osteoarthritis can avoid activities that involve excessive bending or squatting. Additionally, using assistive devices like jar openers, reachers, or long-handled tools can help reduce joint strain during routine tasks.
Assistive Devices and Orthotics
Using assistive devices and orthotics can provide additional support and relief for osteoarthritis-affected joints. For instance, wearing well-cushioned, supportive footwear can reduce pressure on the knees and ankles. Orthotic shoe inserts can help redistribute weight and improve joint alignment. Canes and walkers offer stability while walking and reduce the load on the lower extremities. Healthcare professionals can recommend appropriate assistive devices based on an individual's specific needs and joint involvement.
Adequate Rest and Sleep
Proper rest and sufficient sleep are essential for joint recovery and overall well-being. Individuals with osteoarthritis may experience increased joint pain and stiffness after prolonged periods of activity. Adequate rest allows the joints to recover and reduces the risk of overexertion. Improving sleep quality is equally important, as disrupted sleep can worsen pain perception and negatively impact daily function. Creating a comfortable sleep environment and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule can promote better restorative sleep.
Stress Management
Chronic pain and the challenges of living with osteoarthritis can lead to increased stress and anxiety. Stress management techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and relaxation practices, can help individuals cope with the emotional and physical aspects of their condition. Engaging in hobbies, spending time with loved ones, or seeking support from support groups can also contribute to stress reduction and overall well-being.
Smoking Cessation
Quitting smoking is beneficial for overall health, including joint health. Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of developing osteoarthritis and can worsen existing joint symptoms. Smoking cessation not only improves circulation and tissue healing but also reduces inflammation and further damage to the joints.
Implementing these lifestyle modifications as part of a comprehensive osteoarthritis management plan can significantly improve joint function, reduce pain, and enhance overall quality of life. Combining these lifestyle changes with appropriate medical treatments and therapies can lead to more effective and long-lasting results for individuals living with osteoarthritis.
Medications for Osteoarthritis
Medications play a vital role in managing osteoarthritis symptoms, providing relief from pain and inflammation, and improving joint function. Various medications are available, and the choice of treatment depends on the severity of symptoms, individual health conditions, and other factors. It's essential to work closely with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable medication regimen. Here are some of the commonly used medications for osteoarthritis:
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
Over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers, such as acetaminophen, are often the first-line treatment for mild to moderate osteoarthritis pain. Acetaminophen helps reduce pain and fever by affecting the brain's perception of pain. It is generally well-tolerated and has fewer gastrointestinal side effects compared to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). However, it's essential to follow the recommended dosage to avoid potential liver damage.
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs are a class of medications that help relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and lower fever. They work by blocking the production of prostaglandins, which are chemicals that promote inflammation in the body. Common NSAIDs include ibuprofen, naproxen, and aspirin. While effective in managing osteoarthritis pain, long-term use of NSAIDs may cause gastrointestinal irritation and increase the risk of stomach ulcers or bleeding. It's crucial to use NSAIDs under medical supervision and discuss any existing health conditions or medications that may interact with them.
Topical Medications
Topical medications, such as creams, gels, or patches, containing ingredients like capsaicin or menthol, can provide localized pain relief. These products are applied directly to the skin over the affected joint, delivering medication directly to the site of pain. Capsaicin, derived from chili peppers, works by desensitizing nerve receptors, reducing the sensation of pain. Menthol provides a cooling effect, which can help alleviate pain and discomfort. Topical medications are particularly useful for individuals who cannot tolerate oral medications or have specific joint pain sites that require targeted treatment.
Intra-articular Injections
In cases where oral medications are not providing sufficient pain relief, intra-articular injections may be considered. These injections involve delivering medication directly into the affected joint to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. Two common types of intra-articular injections used for osteoarthritis are:
- Corticosteroid Injections: Corticosteroids are potent anti-inflammatory medications that can provide rapid pain relief. These injections are particularly effective for acute flare-ups of osteoarthritis symptoms. However, repeated use of corticosteroids may have long-term side effects, and their use should be limited to a few times per year.
- Hyaluronic Acid Injections: Hyaluronic acid is a substance naturally present in joint fluid, providing lubrication and shock absorption. Injections of synthetic hyaluronic acid can supplement the joint's natural fluid and reduce friction, thereby easing pain and improving joint movement. The benefits of hyaluronic acid injections may last for several months.
Alternative Therapies
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is an ancient practice that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. It is believed to stimulate the body's natural pain-relieving mechanisms and promote overall well-being.
Chiropractic Care
Chiropractic care focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of musculoskeletal disorders, including osteoarthritis. Spinal manipulation and manual therapies can help improve joint function and reduce pain.
Herbal Supplements
Certain herbal supplements, such as ginger, turmeric, and Boswellia serrata, have shown potential in reducing inflammation and relieving osteoarthritis symptoms. However, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating them into your treatment plan.
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)
TENS therapy involves applying low-voltage electrical currents to the skin, which can help relieve pain by disrupting pain signals. TENS devices are portable and can be used at home under proper guidance.
Surgical Interventions
Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that allows a surgeon to visualize, diagnose, and treat joint conditions. It involves inserting a small camera and surgical instruments through tiny incisions to remove damaged cartilage or repair joint structures.
Joint Replacement Surgery
Joint replacement surgery, such as hip or knee replacement, is considered when conservative treatments no longer provide relief. In these procedures, the damaged joint surfaces are replaced with artificial implants to restore function and reduce pain.
Osteotomy
Osteotomy involves surgically realigning the bones to shift the weight-bearing load away from the damaged joint area. This procedure is commonly performed on the knee to alleviate pain and delay the need for joint replacement.
Cartilage Repair Procedures
Various cartilage repair procedures, such as microfracture, autologous chondrocyte implantation, or mosaicplasty, aim to stimulate the growth of new cartilage or replace damaged cartilage with healthy tissue.
Self Care Approaches
Heat and Cold Therapy
Heat and cold therapy can provide temporary relief for osteoarthritis symptoms. Applying heat, such as using heating pads or warm towels, can help relax muscles and reduce stiffness. Cold therapy, like ice packs or cold compresses, can numb the area and reduce inflammation.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for managing osteoarthritis. Excess weight adds stress to the joints, exacerbating symptoms. A balanced diet and regular exercise can help individuals achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
Stress Management Techniques
Chronic pain can contribute to stress and negatively impact overall well-being. Implementing stress management techniques like meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies can help reduce stress and enhance the ability to cope with osteoarthritis pain.
Conclusion
Living with osteoarthritis can be challenging, but with the right treatment approach, individuals can manage their symptoms effectively and improve their quality of life. From lifestyle modifications and medications to alternative therapies and surgical interventions, there are various options available to tailor a treatment plan to each person's unique needs. It is essential for individuals with osteoarthritis to work closely with their healthcare providers to find the best combination of treatments for their specific condition.
FAQs
- Is osteoarthritis a curable condition? Osteoarthritis is not curable, but its symptoms can be managed with appropriate treatments.
- Are there any side effects of long-term NSAID use for osteoarthritis? Yes, long-term NSAID use can lead to stomach ulcers, gastrointestinal bleeding, and kidney problems. It's essential to use them under medical supervision.
- Can stem cell therapy completely regenerate damaged cartilage? While stem cell therapy shows promise in regenerating tissue, more research is needed to determine its long-term effectiveness fully.
- What is the recovery time for joint replacement surgery? The recovery time varies depending on the type of surgery and the individual's overall health. It may take several weeks to several months to regain full function.
- Is it safe to combine different osteoarthritis treatments? Combining treatments should always be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Disclaimer:
Information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. If you suspect you have osteoarthritis arthritis or are experiencing joint pain, consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment. Remember to always prioritize your health and well-being.